Understanding the financial landscape often involves navigating a complex web of numbers, codes, and procedures. One crucial element within this system is the bank routing number, a nine-digit code that plays a vital role in identifying the financial institution where your account is held. This article will delve into the importance of bank routing numbers, explaining what they are, how they work, and why they are essential for a multitude of financial transactions, from direct deposits and wire transfers to bill payments and automatic withdrawals. Gaining a strong grasp of routing numbers is crucial for anyone participating in the modern banking system.
Whether you’re setting up direct deposit, receiving a wire transfer, or simply writing a check, bank routing numbers are essential for ensuring that funds are transferred accurately and efficiently. A routing number acts as an address for your bank, directing transactions to the correct financial institution. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of routing numbers, examining their structure, significance, and practical applications. By the end of this article, you will possess a comprehensive understanding of bank routing numbers and why they matter in your daily financial life.
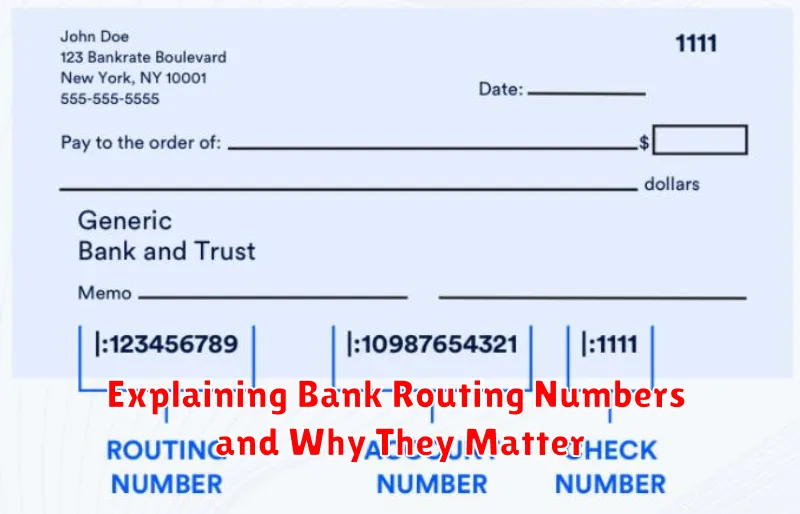
What Is a Bank Routing Number?
A bank routing number is a nine-digit code used to identify a specific financial institution within the United States. It acts like an address for your bank, enabling electronic transfers of funds between banks for transactions like direct deposits, wire transfers, and bill payments. Each bank has its own unique routing number, ensuring that money is sent to the correct destination.
Sometimes referred to as an RTN, routing transit number, or ABA routing number, this code plays a crucial role in the smooth functioning of the US financial system.
How It Differs from Account Numbers
While both routing and account numbers are crucial for transactions, they serve distinct purposes. A routing number identifies the financial institution, like a home address for your bank. It directs transactions to the correct bank.
Your account number, on the other hand, specifies your individual account within that institution. Think of it as your apartment number within the building. It pinpoints where your funds reside.
Where to Find Your Routing Number

Locating your routing number is straightforward. Several readily accessible resources provide this crucial information. You can typically find your routing number on your checks. Look for the nine-digit number printed at the bottom left corner. Alternatively, your bank statements will also display your routing number, often alongside your account number.
If you prefer digital access, online banking platforms and mobile banking apps typically display your account and routing numbers. These can often be found within the account details or profile sections.
Finally, your bank’s official website usually provides a list of routing numbers by state or region. This can be useful if you are unable to access your checks or account statements.
When You’ll Need to Use It
You’ll encounter routing numbers in various financial transactions. Most often, you’ll need it for direct deposits, such as receiving your paycheck or government benefits.
Additionally, electronic bill payments, wire transfers, and setting up automatic payments will require a routing number. It’s also essential when transferring money between your accounts at different financial institutions.
Routing Numbers in Domestic vs. International Transfers
Routing numbers play a crucial role in domestic bank transfers within the United States. They identify the specific financial institution involved, ensuring funds reach the correct destination. For transfers within the US, a nine-digit routing number is sufficient.
However, for international transfers, routing numbers alone are typically insufficient. These transfers usually require additional information, such as the SWIFT code, to identify the recipient bank internationally. The SWIFT code operates similarly to a routing number but on a global scale. Some US banks may also use their SWIFT code for international transfers even when sent from a US bank.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When dealing with routing numbers, accuracy is crucial. Transposing digits is a common error that can lead to processing delays or rejected payments. Always double-check the number you’ve entered against your bank records.
Using the wrong routing number is another significant mistake. Different banks have different routing numbers, and using an incorrect one can cause funds to be misdirected. Verify the correct routing number for your specific bank and account type, especially for wire transfers or ACH transactions.
Outdated information can also cause problems. If you’ve recently switched banks or accounts, ensure you are using the current routing number. Refer to your most recent bank statement or contact your bank directly for the most up-to-date information.
How to Keep It Secure
Protecting your bank routing number is crucial for your financial safety. Never share this number over the phone or via email unless you initiated the contact with a verified institution. Be wary of unsolicited requests.
When banking online, ensure the website uses HTTPS, indicated by a lock icon in the address bar. This signifies a secure connection. Regularly monitor your bank statements for any unauthorized transactions. Report suspicious activity immediately.