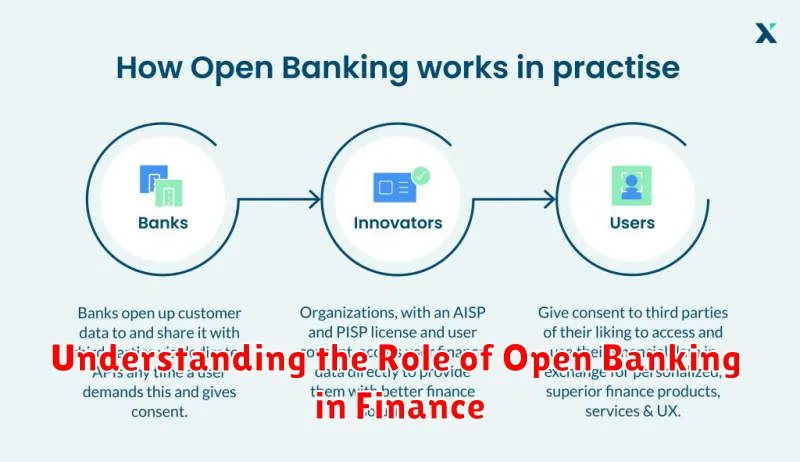
The financial landscape is rapidly evolving, and at the forefront of this transformation is open banking. This innovative approach to financial data sharing is revolutionizing how we interact with our finances, promising greater transparency, competition, and control for consumers and businesses alike. Understanding the role of open banking in finance is crucial for navigating this new era of financial services, whether you’re a seasoned financial professional, a tech enthusiast, or simply someone looking to better manage their money. This article will explore the core principles of open banking, its impact on traditional banking, and the potential it holds for the future of finance.
Open banking, powered by secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), allows third-party providers to access consumer banking data with their explicit consent. This data sharing empowers consumers to leverage innovative financial products and services, from personalized budgeting tools and robo-advisors to streamlined loan applications and sophisticated fraud detection. By fostering greater competition and innovation in the financial sector, open banking is driving the development of more efficient, customer-centric solutions. Furthermore, it provides individuals and businesses with unprecedented control over their financial data, enabling them to make more informed decisions and optimize their financial well-being. This article will delve deeper into the mechanics of open banking, examining its benefits and challenges, as well as its potential to reshape the financial ecosystem.
What Is Open Banking?
Open banking is a banking practice that provides third-party financial service providers open access to consumer banking, transaction, and other financial data from banks and non-bank financial institutions through the use of application programming interfaces (APIs).
Consumers authorize this data sharing through their bank or financial institution. Open banking allows networking of accounts and data across institutions for use by consumers, financial institutions, and third-party service providers.
How It Improves Financial Transparency
Open banking significantly enhances financial transparency by providing consumers with a comprehensive view of their financial data. This aggregated data, accessible through authorized third-party providers, empowers individuals to make more informed decisions.
Furthermore, open banking promotes greater clarity on product pricing and fees. This allows for easier comparison between different financial institutions, fostering competition and driving innovation within the financial sector.
Benefits for Consumers and Developers
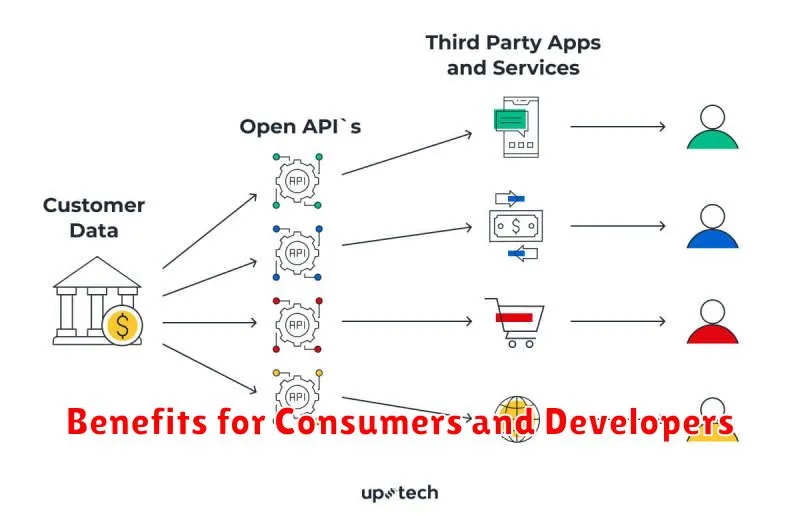
Open banking offers numerous advantages for both consumers and developers. Consumers gain access to innovative financial products and services, fostering increased competition and potentially lower costs. Personalized financial management tools empower consumers to make informed decisions.
Developers benefit from a standardized API framework which facilitates the creation of new applications and services. This, in turn, fosters innovation and growth within the fintech sector. Open banking creates a more dynamic and responsive financial ecosystem.
Data Sharing and Permissions Explained
Open Banking relies on secure data sharing practices. This involves customers granting explicit permission for their financial data to be accessed by authorized third-party providers (TPPs). Consent is paramount, and customers retain full control over which data is shared and with whom. This permission-based access is facilitated through secure APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
Data sharing is not indiscriminate. Customers choose specific data points to share, such as transaction history or account balances, with designated TPPs for specific purposes, like budgeting apps or loan comparison services. This granular control empowers consumers and fosters a more competitive financial landscape.
Security Concerns and Regulatory Standards
Open banking, while offering numerous benefits, raises significant security and privacy concerns. Data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive financial information are primary risks. Therefore, robust security measures are crucial.
Regulatory standards play a vital role in mitigating these risks. These standards define security protocols, data protection requirements, and consumer consent frameworks. Compliance with these standards is essential for building and maintaining consumer trust in open banking ecosystems.
Real-Life Examples of Open Banking
Open Banking fuels a variety of financial applications. One example is account aggregation, where users can view all their accounts from different institutions in one place. This simplifies financial management and provides a holistic view of finances.
Another example is personalized financial advice. By analyzing transaction data, open banking enables tailored recommendations on budgeting, saving, and investing. This empowers users to make informed financial decisions.
Automated bill payments are also facilitated through open banking. Securely connecting to bank accounts allows authorized third-party providers to automate recurring payments, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
How It’s Shaping the Future of Finance
Open banking is poised to revolutionize the financial landscape. By enabling the secure sharing of consumer financial data with third-party providers, it fosters innovation and competition.
This translates to more personalized financial products and services. Consumers can expect tailored financial advice, automated budgeting tools, and streamlined loan applications. Empowerment shifts to the consumer with greater control over their financial data and choices.
Furthermore, open banking is expected to drive efficiency in financial operations. Processes like KYC (Know Your Customer) become simplified, reducing costs for both businesses and consumers. This creates opportunities for new business models and financial services previously unimaginable.