In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, choosing between digital banking and traditional banking can be a pivotal decision. This article delves into the key differences between these two banking models, providing a comprehensive comparison to help you make an informed choice. We’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of each, examining factors such as accessibility, fees, security, and customer service. Understanding the nuances of digital banks versus traditional banks is crucial for navigating the modern world of finance.
Whether you prioritize the convenience of online banking, the personal touch of a brick-and-mortar branch, or the security of established institutions, this article offers valuable insights. We’ll dissect the core functionalities of both digital banking and traditional banking, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses. From mobile check deposits to in-person financial advice, we’ll cover the essential aspects of each banking experience to empower you to choose the best fit for your financial needs. This comparison of digital vs. traditional banking will equip you with the knowledge you need to make a confident decision.
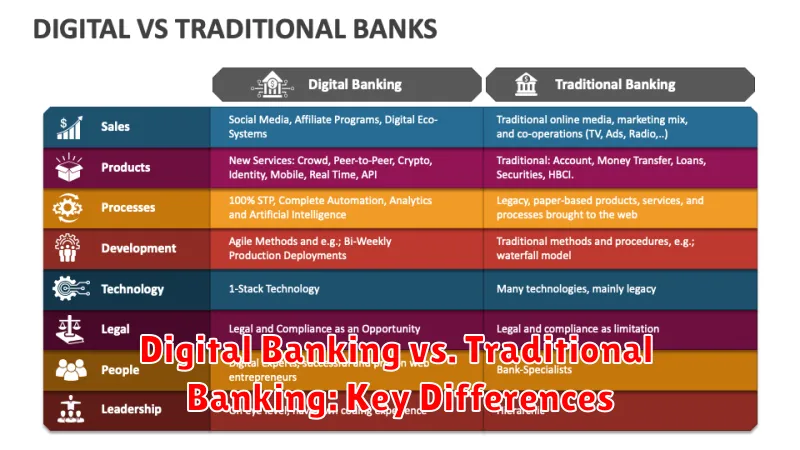
What Defines Digital and Traditional Banking
Traditional banking primarily relies on physical branches and in-person interactions. Customers visit a local branch to open accounts, deposit checks, and conduct most transactions. Services are typically limited to banking hours.
Digital banking, conversely, leverages technology to deliver financial services through online platforms and mobile applications. Customers can access accounts, transfer funds, and manage finances remotely, 24/7. It prioritizes convenience and accessibility.
Branchless Services vs. In-Person Support
A key distinction between digital and traditional banking lies in access to physical branches. Digital banks primarily operate online, offering branchless services accessible 24/7 via websites and mobile apps. This offers convenience and accessibility, but may lack the personalized touch some customers prefer.
Traditional banks maintain a network of physical branches, providing in-person support for complex transactions and personalized financial advice. While offering a more personal experience, branch access is limited by location and operating hours. This can be inconvenient for customers who prefer digital interactions or live outside of branch service areas.
Fee Structures and Account Maintenance
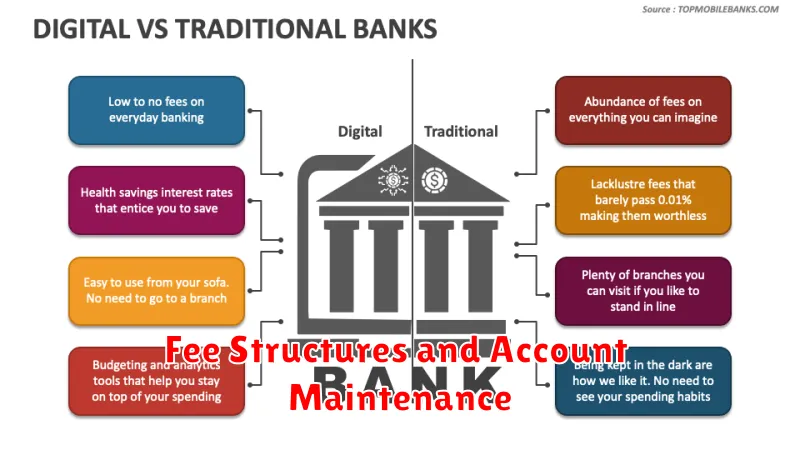
A key difference between digital and traditional banking lies in their fee structures. Digital banks often boast lower or no monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees, and minimum balance requirements. This cost-effectiveness stems from their lower overhead compared to traditional banks with physical branches.
Traditional banks, while sometimes offering fee waivers based on certain criteria, generally have higher fees associated with account maintenance. These fees can vary significantly depending on the type of account and the bank’s policies, so careful comparison is essential.
Transaction Speed and 24/7 Access

A key advantage of digital banking lies in its speed and accessibility. Transactions typically process much faster than in traditional banking, often occurring in real-time.
Furthermore, digital banking platforms offer 24/7 access to accounts. Customers can manage their finances anytime, anywhere, eliminating the constraints of traditional banking hours and physical branch locations.
Customer Experience and App Usability
A key differentiator between digital and traditional banking lies in customer experience. Digital banking offers 24/7 access to accounts via user-friendly mobile apps and websites. This allows for convenient balance checks, transfers, and bill payments from anywhere.
Traditional banking, conversely, often requires physical branch visits during limited business hours. While some traditional banks offer online services, their digital experience often lags behind the intuitive design and functionality of dedicated digital banking platforms.
Security Models Compared
Both digital and traditional banking employ robust security measures, albeit with different approaches. Traditional banking relies heavily on physical security, including vaults, security personnel, and fraud detection departments. Digital banking emphasizes cybersecurity measures like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and real-time transaction monitoring.
While both models face risks, digital banking is more susceptible to phishing and hacking attempts. Conversely, traditional banking remains vulnerable to physical theft and forgery. Both systems continually adapt their security protocols to address emerging threats.
Which One Suits Your Lifestyle?
Choosing between digital and traditional banking hinges on your individual needs and preferences. Consider your comfort level with technology. Are you tech-savvy and prefer managing your finances online? Or do you value in-person interactions and prefer the reassurance of a physical branch?
Think about your accessibility needs. Do you require frequent branch access, or are you comfortable managing your finances remotely? Also, evaluate your financial habits. Do you prefer 24/7 account access and instant transactions, or are you comfortable with traditional banking hours?